 Taipei will soon open a dozen new stations on its mass-transit system, the MRT. Most of the stations will be in the relatively newly developed district of Neihu, with a couple in the Nangang district. It’s the latter two stations I want to focus on:
Taipei will soon open a dozen new stations on its mass-transit system, the MRT. Most of the stations will be in the relatively newly developed district of Neihu, with a couple in the Nangang district. It’s the latter two stations I want to focus on:
- Nangang Software Park
- Taipei Nangang Exhibition Center
Basically, these names suck.
The most obvious problem is that they both are unnecessarily long, which is not a negligible consideration for not only signage but also the MRT’s announcement system, which is in four languages: Mandarin, Hoklo, Hakka, and English. (It takes a while to get through all of those.)
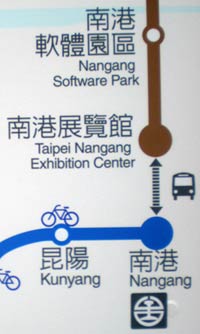
Also, “Nangang Software Park” (Nángǎng Ruǎntǐ Yuánqū 南港軟體園區)? There is no other software park around the MRT system. Just “Software Park” would work better as a name for the station. Accurate, but also short, simple, and distinctive — just what such a name should be.
BTW, this software park is the source of the name for Taipei’s still-not-corrected Park Street signs.
Worse still is “Taipei Nangang Exhibition Center”. First, calling it even “Nangang Exhibition Center” would be bad enough for the same reason that “Nangang Software Park” is unnecessarily wordy: there’s no “exhibition center” anywhere else on the system.
But “Taipei Nangang”? Ugh. That may work in Mandarin, but it’s lousy English. It follows the same unnaturally inverted pattern and redundancy that gave us “Taiwan Taoyuan International Airport,” or, as I like to call it, Chinglish International Airport. (But I do like it better than “Revere the Dictator Chiang Kai-shek International Airport.”)
Here’s a photo of the exhibition building itself (not the MRT station — though those are the MRT tracks behind the barrier in the foreground).

So “Taipei Nangang Exhibition Center” probably is the official name of the complex. But that really doesn’t matter because (1) the MRT station certainly does not have to have the exact same name and (2) the name is just plain stupid.
Above, I mentioned that names for MRT stations should be “accurate, but also short, simple, and distinctive.” Sticking “Taipei Nangang” in front of “Exhibition Center” makes the name clumsy and less distinctive, especially since the two MRT stations closest to “Taipei Nangang Exhibition Center” are called “Nangang” and “Nangang Software Park”.
Nangang, Nangang, Nangang — yeah, we get it: They’re in Nangang.
Perhaps the MRT would like to change other names to be similarly useful. For example, instead of “Chiang Kai-shek Memorial Hall” we could have “Taipei Zhongzheng Chiang Kai-shek Memorial Hall;” and in place of, say, “Xindian City Hall” we could have “Taipei County Xindian Xindian City Hall.” (More about the Xindian City Hall station in another post.)
But perhaps those names aren’t nearly informative enough. According to the MRT’s way of thinking, people might still be confused about the location. How about, say, “Planet Earth Northern Hemisphere Asia East Asia Taiwan Taipei Zhongzheng Chiang Kai-shek Memorial Hall” and “Planet Earth Northern Hemisphere Asia East Asia Taiwan Taipei County Xindian Xindian City Hall,” etc.?
I’m happy to report that even the MRT seems to have some reservations about ridiculously long names — at least when those names are in Mandarin. Note the photo of part of the route map (top right of this post). The Mandarin name for “Taipei Nangang Exhibition Center” is Nángǎng Zhǎnlǎnguǎn (南港展覽館), not Táiběi Nángǎng Zhǎnlǎnguǎn (台北南港展覽館). (I didn’t crop any characters from the left of the station name.) So why is “Taipei” in the English version but not in the Mandarin one? Does the city government believe that foreigners are so stupid that they fail to comprehend that the Taipei MRT system is indeed in the Taipei metropolitan area? If so, then maybe they should be giving consideration to my idea of putting at least “Planet Earth Northern Hemisphere Asia East Asia Taiwan Taipei” in front of all the names in the city of Taipei. This could come in in several versions:
- “Planet Earth Northern Hemisphere Asia East Asia Taiwan, Republic of China, Taipei” — for pan-blue traditionalists
- “Planet Earth Northern Hemisphere Asia East Asia Taiwan, which is really a country and not a part of China, Taipei” — for the pan-green crowd, and
- “Planet Earth Northern Hemisphere Asia East Asia China Chinese Taipei Taipei” — for the unificationists and those who like to “q?n Zh?ngguó“
Then administrations could have fun changing from one system to another, depending on who was in power.
There’s more to say about this topic (e.g., how the names of stations such as Taipei Zoo, Taipei City Hall, and Xindian City Hall Office do or don’t fit into this pattern). But I’ve already written enough for one post.
And in case anyone is wondering: Yes, I have brought my concerns to the attention of the officials of the MRT. They don’t care. Does anyone have contacts in the media or with politicians?

















