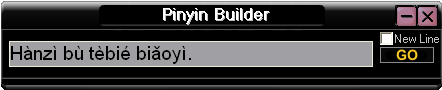
Professor Qián Nǎiróng (Qian Nairong / 錢乃榮) of Shanghai University has just issued free software to help with the writing of Shanghainese (上海话). People may now download the 1.3 MB zip file of the program.
Some examples:
shanghe 上海
shanghehhehho 上海闲/言话(上海话)
whangpugang 黄浦江
suzouhhu苏州河
shyti 事体(事情)
makshy 物事(东西)
bhakxiang 白相(玩)
dangbhang 打朋(开玩笑)
ghakbhangyhou 轧朋友(交朋友)
cakyhangxiang 出洋相(闹笑话,出丑)
linfhakqin 拎勿清(不能领会)
dhaojiangwhu 淘浆糊(混)
aoshaoxhin 拗造型(有意塑造姿态形象)
ghe 隑(靠)
kang 囥(藏)
yin 瀴(凉、冷)
dia 嗲
whakji 滑稽
The program offers two flavors of romanization. Here are some examples of the differences between the two styles:
| New Folk |
Old Timers |
makshy 物事(东西)
bhakxiang 白相(玩)
dangbhang 打朋(开玩笑)
ghakbhangyhou 轧朋友(交朋友)
cakyhangxiang 出洋相(闹笑话,出丑)
linfhakqin 拎勿清(不能领会)
|
mekshy 物事(东西)
bhekxian 白相(玩)
danbhan 打朋(开玩笑)
ghakbhanyhou 轧朋友(交朋友)
cekyhanxian 出洋相(闹笑话,出丑)
linfhekqin 拎勿清(不能领会)
|
Here’s a brief story on this:
Xiànzài, wǒmen zài wǎngluò zhōng liáotiān de shíhou yuèláiyuè duō de péngyou dōu kāishǐ xǐhuan yòng Shànghǎihuà. Dànshì yǒushíhou shìbushì juéde xiǎng biǎodá dehuà bùzhīdào zěnme dǎ, nòng de yǒudiǎn bùlúnbùlèi ne? Xiànzài, yī ge kěyǐ qīngsōng dǎchū Shànghǎihuà de chéngxù chūlai le.
Jīngguò liǎng nián nǔlì, Shànghǎi dàxué Zhōngwénxì Qián Nǎiróng jiàoshòu jí tā de yánjiūshēng hé dādàng zhōngyú yú běnyuè wánchéng le Shànghǎihuà shūrùfǎ de zhìzuò. Zhíde guānzhù de shì, zhè tào shūrùfǎ hái bāokuò xīn-lǎo liǎng ge bǎnběn, 45 suì yǐshàng de lǎo Shànghǎi rénhé niánqīng yī dài de Shànghǎirén dōu kěyǐ zhǎodào zìjǐ de “dǎfǎ.”
Háishi tóngyàng 26 ge zìmǔ de jiànpán, 8 yuè 1 rì qǐ xiàzài le Shànghǎihuà shūrùfǎ zhīhòu, nín jiù kěyǐ tōngguò shūrù “linfhakqin” dǎchū “līn wù qīng,” shūrù “dhaojiangwhu” dǎchū “táo jiànghu” děng yuánzhī yuán wèi de Shànghǎihuà le. Zuótiān, jìzhě tíqián xiàzài dào gāi ruǎnjiàn. Ànzhào shǐyòng shuōmíng, yòng quánpīn de fāngshì chángshì shūrù “laoselaosy” zhèxiē zìmǔ, píngmù shàng, lìjí chūxiàn le “lǎo sānlǎo sì” (Shànghǎihuà, yìsi shì “màilǎo, chōng lǎochéng de yàngzi”).
Jùxī, yóuyú Shànghǎihuà yǔ Pǔtōnghuà de dúfǎ yǒusuǒbùtóng, suǒyǐ zài pīnyīn pīnxiě fāngshì shàng háishi xūyào shǐyòng shuōmíng de bāngzhù. Bǐrú jìzhě fāxiàn, fánshì yǔ Pǔtōnghuà shēngmǔ, yùnmǔ xiāngtóng de zì, zài Shànghǎihuà shūrùfǎ zhōng zuìzhōng yòng de háishi Pǔtōnghuà pīnyīn, bùtóng de zé cǎiyòng Shànghǎihuà shūrùfǎ de pīnxiě fāngshì. Rú “chénguāng” de “chén,” “huātou” de “tóu” dōu fāchéng zhuóyīn, Shànghǎihuà pīnyīn shūrùfǎ zhōng yàozài shēngmǔ zhōng jiā yī ge zìmǔ h, pīnchéng “shen,” “dhou;” fánshì rùshēng zì, zé zài pīnyīn hòu jiā zìmǔk, rú “báixiāng” de “bái” jiù pīnchéng bhek.
Bùguò, dàjiā bùyào juéde tài nán. Jìzhě fāxiàn, Shànghǎihuà shūrùfǎ yǔ Pǔtōnghuà de shūrùfǎ zuìdà xiāngtóng zhī chǔzài yú, zhǐyào liánxù shūrù shēngmǔ hé yùnmǔ jiù kěyǐ, bùxū shūrù shēngdiào. Cǐwài, Shànghǎihuà pīnyīn shūrù xìtǒng háiyǒu lèisì “zhìnéng” yōudiǎn, kěyòng suōlüè fāngshì bǎ cíyǔ pīnxiě chūlai.
Zhǔchí Shànghǎihuà shūrùfǎ kāifā de Shànghǎi dàxué Zhōngwénxì Qián Nǎiróng jiàoshòu gàosu jìzhě, zhè tào shūrùfǎ bùjǐn néng dǎchū Shànghǎihuà dà cídiǎn zhōng 15,000 duō ge cítiáo, érqiě hái néng yòng Shànghǎihuà pīnyīn dǎchū Shànghǎihuà zhōng shǐyòng zhe de, yǔ Pǔtōnghuà cíyì xiāngtóng dàn yǔyīn bùtóng de chángyòng cíyǔ. Rú “Huángpǔ Jiāng” shūrù “whangpugang” , “lǐxiǎng” zéshì lixiang děng, gòngjì 10,000 duō ge cítiáo.
sources:
 If you are using one or more programs from the Chinese Key family of software, you should definitely update if you haven’t in the past few months, as some significant improvements have been made.
If you are using one or more programs from the Chinese Key family of software, you should definitely update if you haven’t in the past few months, as some significant improvements have been made.