With Chinese characters getting used to demonstrate that “ancient Chinese” is the “language of God,” it’s only fair that the Japanese get some special etymologies out of kanji as well. (At No-sword, of course.)
Category Archives: Japanese
85 percent of Japanese report weakening of ability to write kanji: poll
I may have understated the headline by using “weakening.” Regardless, though, the figures are dramatic.
People are becoming accustomed to computer-aided input of kanji and thus forgetting how to be able to write them by hand. This is only going to get worse, not better.
For a brief English article on this, see the link below.
「パソコンを始めて漢字が書けなくなった70%、読める漢字が増えた15%」。
6月に行った調査 ではこんな結果が出ているが、最新の調査はどうだろうか。「漢字の日」である12月12日、ニンテンドー DS 用ソフト「 漢検DS 」が、漢字に関する意識調査の結果を発表した。同調査は10~15歳の“こども”400名、35~40歳の“大人”400名を対象としている。
調査によれば、「漢字を書く機会が減ったと感じている」大人が93%、「ここ何年かで自分の漢字力が低下したと感じている」大人が85%にものぼり、多くの大人が漢字を書く機会が減り、漢字が書けなくなったと感じていることがわかった。
このような結果にもかかわらず、こども世代の過半数以上は「分からない漢字は両親に聞く」と考えている。一方の大人世代では、4人に1人が「漢字を書けなくて恥を書いたシチュエーション」として、「こどもなど、人に聞かれてわからなかった時」と答えた。「親は漢字が分かるもの」というこどもの期待と、親の能力には大きな乖離があるようだ。
漢字力が低下した原因について尋ねるたところ(複数回答)、最も多かった回答は「PC をよく使うから」で87.4%。続いて「携帯電話(携帯メール)をよく使うから」(43.8%)、「年齢をおうことによる記憶力の低下」(41.8%)の順となった。
早稲田大学笹原宏之助教授はこう分析する。「漢字教育が漢字についての応用力を育てるような体系的なものとして行われておらず、また日常生活でも本や新聞などの紙面よりも、テレビやパソコンなど画面の上で漢字を書いたり見たりする機会が増えたためだ」
自分の漢字力を知る方法としては、大人、こどもともに、1位「漢字検定」、2位「漢字勉強用ゲームソフト」、3位「漢字問題集」という結果となった。また、こどもが漢字勉強用ゲームソフトで漢字を勉強することについては、大人の48%が賛成と回答している。
笹原助教授は漢字力低下の要因を、PC などの普及による漢字を書く行為のデジタル化に見出したが、その低下した漢字力を向上させるための学習方法にもデジタル化の波が及んでいるのかもしれない。
ちなみになぜ12月12日が「漢字の日」かといえば、1995年に財団法人日本漢字能力検定協会が「いい(1)じ(2)いち(1)じ(2)」(いい字1字)の語呂合わせで設定したからだという。
sources:
- 「漢字が書けなくなった」大人85%――漢字力低下要因、学習方法ともに“デジタル化”, December 12, 2006
- Japanese Losing Their Handwriting Skills, Zaman (Istanbul), December 12, 2006
new book on language policy in Taiwan during the Japanese era
 While browsing at Eslite the other day I happened across a new book that sounds interesting: Tónghuà de tóngchuángyìmèng: Rìběn zhì shíqī Táiwān de yǔyán zhèngcè, jìndài huà yǔ rèntóng (同化的同床異夢: 日治時期臺灣的語言政策、近代化與認同), by Chen Pei-feng (Chén Péi-fēng / 陳培豐).
While browsing at Eslite the other day I happened across a new book that sounds interesting: Tónghuà de tóngchuángyìmèng: Rìběn zhì shíqī Táiwān de yǔyán zhèngcè, jìndài huà yǔ rèntóng (同化的同床異夢: 日治時期臺灣的語言政策、近代化與認同), by Chen Pei-feng (Chén Péi-fēng / 陳培豐).
Although the book is written in Mandarin and has essentially no English, it has a strange but intriguing English title: The Different Intentions Behind the Semblance of “Douka”: The Language Policy, Modernization, and Identity in Taiwan during the Japan-Ruling Period. This doesn’t quite match the Mandarin.
I’d be interested in hearing from anyone who has read this.
make romanizations, not war
 While a lot of things might be unusual about this old print of a Japanese soldier having sex with or simply raping a Western soldier, what particularly startled me is the use of romanization. Given that much of the text in the full image (note: definitely not safe for work) isn’t accompanied by romanization, it appears the intent is to help indicate which lines are being said by the Westerner. (But I can’t read Japanese, so I don’t know for sure.)
While a lot of things might be unusual about this old print of a Japanese soldier having sex with or simply raping a Western soldier, what particularly startled me is the use of romanization. Given that much of the text in the full image (note: definitely not safe for work) isn’t accompanied by romanization, it appears the intent is to help indicate which lines are being said by the Westerner. (But I can’t read Japanese, so I don’t know for sure.)
Has anyone noticed this practice — the romanization, y’all — in other Japanese prints?
Commenters on Eros Blog (again, not safe for work) translate the text and place the cartoon from the time of the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–05.
chlorinated alphabet
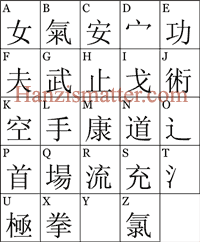 Tian at Hanzismatter always manages to find good stuff. But this time, with the help of Alan Siegrist, he’s outdone himself. I’ve got tears streaming down my face because I’ve been laughing so hard at the font of random characters and so-called radicals that some people have apparently been mistaking for a phonetic guide to Chinese characters.
Tian at Hanzismatter always manages to find good stuff. But this time, with the help of Alan Siegrist, he’s outdone himself. I’ve got tears streaming down my face because I’ve been laughing so hard at the font of random characters and so-called radicals that some people have apparently been mistaking for a phonetic guide to Chinese characters.
My title for this entry is in reference to the character given when the letter Z is typed: 氯. This is lǜ, which means “chlorine.”
Festschrift for John DeFrancis now available for free
Most readers of Pinyin News will already know of John DeFrancis, editor of the ABC Chinese-English Comprehensive Dictionary and author of The Chinese Language: Fact and Fantasy and many other important works. (If you haven’t read The Chinese Language: Fact and Fantasy yet, order it now.)
In recognition of the 95th(!) birthday today of Professor DeFrancis, Sino-Platonic Papers is rereleasing Schriftfestschrift: Essays in Honor of John DeFrancis on His Eightieth Birthday. Previously, this important compilation, which runs more than 250 pages, was available only in a printed edition priced at US$35. The fifteenth-anniversary edition, however, is being released for free as a PDF (15 MB — so have a fast Internet connection, or a lot of patience).
I’d like to draw special attention to an article written in Pinyin: “Hanzi Bu Tebie Biaoyi,” by Zhang Liqing. (Zhang’s work also appears here on Pinyin Info, in her translations of The Historical Evolution of Chinese Languages and Scripts and of the amazing Comparing Chinese Characters and a Chinese Spelling Script — an evening conversation on the reform of Chinese characters.)
Feel free to print out a copy of the Schriftfestschrift for your own use or for inclusion in a library. Just don’t sell it.
The original publication contained several color photos. I’ll add those later. Also, the English tex is searchable to some degree, as I used OCR after scanning these pages; but the results weren’t perfect.
Here are the contents:
- Tabula Gratulatoria
- Introduction, by Victor H. Mair
- Publications of John DeFrancis
- Hanzi Bu Tebie Biaoyi, by Zhang Liqing
- Typology of Writing Systems, by Zhou Youguang
- Dui Hanzi de Jizhong Wujie, by Yin Binyong
- The Information Society and Terminology, by Liu Yongquan
- A Bilingual Mosaic, by Einar Haugen
- The Polysemy of the Term Kokugo, by S. Robert Ramsey
- Memorizing Kanji: Lessons from a Pro, by J. Marshall Unger
- Why Chinese Is So Damn Hard, by David Moser
- Ethnolinguistic Notes on the Dungan, by Lisa E. Husmann and William S-Y. Wang
- Korean Views on Writing Reform, by Wm. C. Hannas
- Language Policies and Linguistic Divergence in the Two Koreas, by Ho-min Sohn
- Okinawan Writing Systems, Past, Present, and Future, by Leon A. Serafim
- Proposal of a Comparative Study of Language Policies and Their Implementation in Singapore, Taiwan, and China (PRC), by Robert L. Cheng
- The Topical Function of Preverbal Locatives and Temporals in Chinese, by Feng-fu Tsao
- Yes-No Questions in Taipei and Peking Mandarin, by Robert M. Sanders
- Patronizing Uses of the Particle ma: Bureaucratic Chinese Bids for Dominance in Personal Interactions, by Beverly Hong Fincher
- Gender and Sexism in Chinese Language and Literature, by Angela Jung-Palandri
- A zhezi Anagram Poem of the Song Dynasty, by John Marney
- Some Remarks on Differing Correspondences in Old Chinese Assumed to Represent Different Chinese Dialects, by Nicholas C. Bodman
- Can Taiwanese Recognize Simplified Characters?, by John S. Rohsenow
- Simplified Characters and Their (Un)relatedness, by Chauncey C. Chu
- The Teaching of Culture and the Culture of Teaching: Problems, Challenges, and Opportunities in Language Instruction, by Eugene Eoyang
- The Culture Component of Language Teaching, by Kyoko Hijirida
- Thinking About Prof. John DeFrancis, by Apollo Wu
- Wo suo Renshi de De Xiansheng, by Chih-yu Ho
- Two Poems for Professor John DeFrancis, by Richard F. S. Yang
- Announcement, by Stephen Fleming
Happy birthday, John! And many happy returns!
kanji conversions cause crash
This is a weird one: Sharp Corp. has acknowledged that more than 10 million of its cell phones have a “software glitch that disables the handsets when certain hiragana phrases are converted into kanji when writing e-mail.”
The phrases known to freeze the phones are: “mirare makuccha,” which roughly means “people’s eyes were fixed on me,” and “kazega naori kaketa,” meaning, “I was recovering from a cold,” according to Nikkei Net, a Web-based business and information technology news site.
I’m not sure I could come up with a proper comment on this even if I didn’t have a bad case of jet lag.
sources:
- Sharp software glitch freezes cell phones, Japan Times, July 20, 2006
- PEOPLE’S EYES WERE FIXED ON ME, July 20, 2006
- 「みられまくっちゃ」でフリーズ――シャープ製端末搭載shoin4に不具合か?, HiRO’s Blog
learn kanji through noh?
Studying kanji while taking in a Japanese noh drama — what could more exciting? Heh.
A common problem for those new to Japanese traditional performing arts is that–even for native Japanese speakers–it is hard to understand the story and old-fashioned language used in noh recitation or gidayu, a form of narrative chanting that accompanies bunraku performances. With a view to solving this problem, there has been a marked increase in productions using Japanese subtitles at the National Theatre in Tokyo and National Bunraku Theatre in Osaka. The National Noh Theatre in Tokyo also plans to make greater use of subtitles on screens it will introduce in autumn.
The new computer-controlled system to be introduced at the National Noh Theatre in Tokyo, where prior improvements to seats and other theater facilities are scheduled for completion in August and September, will allow Japanese subtitles to be displayed on flat-panel screens installed in seat backs.
“We will provide Japanese and English subtitles for the time being, although the system will allow us to use four channels in total,” said an official at the noh theater. Noh recitation will be displayed as it is in Japanese, while the plot of the play and a briefing on scenes will be provided in English along with a translation of the recitation….
Some bunraku performers at first questioned why Japanese subtitles were necessary since most audience members are Japanese.
“But they don’t voice such objections any more. Some even say the subtitles are useful in learning kanji…,” said Takemoto Sumitayu, a bunraku narrator and a living national treasure.
The National Bunraku Theatre hopes that the service “will help overcome the image of traditional performing arts as hard to understand.”
I suppose as long as the chairback is below the stage, the text would still be subtitling. But I can’t help but wonder if there’s a more precise term. It’s not likely to be real captioning. And what’s the word for texts that are presented on the sides of stages?
source: Does Japanese theater need Japanese subtitles?, Daily Yomiuri, July 8, 2006
