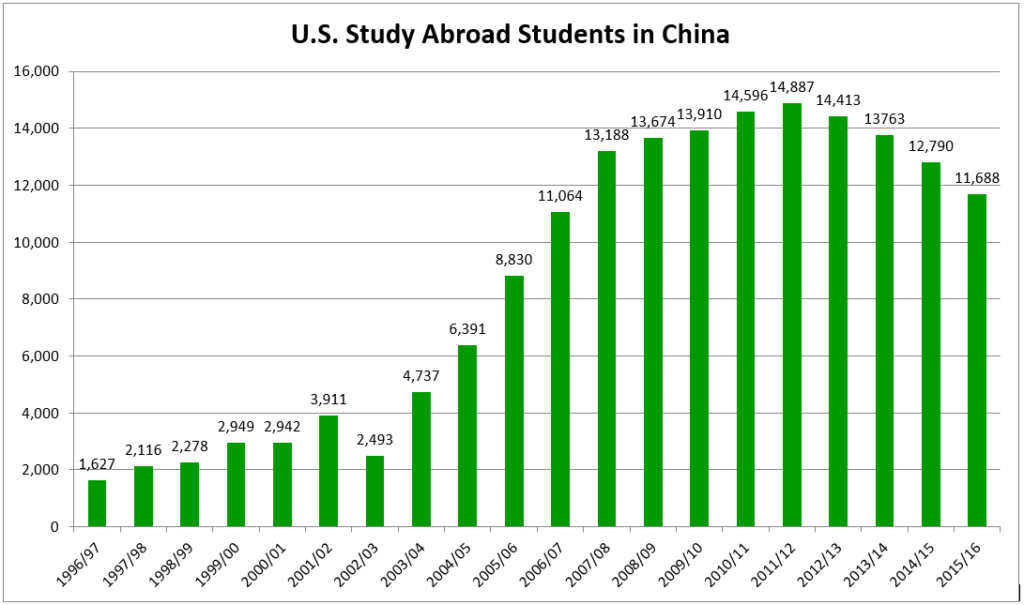
North Korea is a scary, scary, scary place. Fortunately, at least for those of us not living in that People’s Paradise, every so often the country also provides important linguistic tips, which I am duty-bound to pass along to you.
For example, did you know that names without final consonants are “anti-socialist”? The wise authorities in North Korea have reportedly come to that conclusion and are presently dedicated to the task of cleansing that evil. Since October, “notices have been constantly issued at the neighborhood-watch unit’s residents’ meeting to correct all names without final consonants. People with names that don’t have a final consonant have until the end of the year to add political meanings to their name to meet revolutionary standards,” a resident of North Korea’s North Hamgyong told Radio Free Asia.
In meetings and public notices, officials have gone so far as to instruct adults and children to change their names if they are deemed too soft or simple …, another source said….
The government has threatened to fine anyone who does not use names with political meanings, a resident in the northern province of Ryanggang told RFA on condition of anonymity to speak freely.
Naturally, it would be unwise to adopt any sort of name that reminds the government authorities of names in South Korea or elsewhere.
In the past, North Koreans were encouraged to give their children patriotic names that held some ideological or even militaristic meaning, such as Chung Sim (loyalty), Chong Il (gun), Pok Il (bomb) or Ui Song (satellite).
In recent years, though, as the county has become more open to the outside world, North Koreans have been naming their children gentler, more uplifting names that are easier to say, such as A Ri (loved one), So Ra (conch shell) and Su Mi (super beauty), sources inside the country say.
Instead of names that end on harder sounding consonants, children are being given names that end in softer vowels, which is more like names given to children in South Korea.
But recently, North Korean authorities are clamping down on this trend, requiring citizens with the softer names to change to more ideological ones, and even their children’s names, if they aren’t “revolutionary” enough, the sources say.
source: North Korea forcing citizens to change their names to sound more ideological, Radio Free Asia, November 30, 2022
related article in Korean: “남한식 이름 불가” 북, 혁명적 개명 강요 (“South Korean names are not allowed.” North Forces Revolutionary Name Changes), Radio Free Asia, November 28, 2022
Further reading: “북 채택 예고한 ‘평양문화어보호법’, 사상·정신적 이완 방지 조치” (North Korea to adopt Pyongyang Cultural Language Protection Act to prevent ideological and mental relaxation), Radio Free Asia, December 7, 2022.