Columbia University Press recently published what I hope will become recognized as the standard English translation of the Art of War (Sūnzǐ Bīngfǎ / 孫子兵法). This is by my friend Victor H. Mair of the University of Pennsylvania’s department of Asian and Middle Eastern studies.
Columbia University Press recently published what I hope will become recognized as the standard English translation of the Art of War (Sūnzǐ Bīngfǎ / 孫子兵法). This is by my friend Victor H. Mair of the University of Pennsylvania’s department of Asian and Middle Eastern studies.
With the permission of the author and publisher, I offer below two excerpts from this work.
But first a bit of information from the publisher’s page for this title.
Victor Mair’s translation is the first to remain true to the original structure and essential style of the text.
Mair’s fidelity to the original, along with his insightful commentary and reliance on archaeologically recovered manuscripts, breaks new ground in solving The Art of War‘s difficult textual and contextual problems. He confronts complex questions concerning the authorship of the work, asserting that Sun Wu, a supposed strategist of the Spring and Autumn period (770-476 B.C.E.) to whom the text is traditionally attributed, never existed. Instead, Mair claims that The Art of War coalesced over a period of around seventy-five years, from the middle of the fourth century to the first quarter of the third century B.C.E.
Mair also reveals the way The Art of War reflects historical developments in technological and military strategy in civilizations throughout Eurasia, especially in regards to iron metallurgy. He demonstrates the close link between the philosophy in The Art of War and Taoism and discusses the reception of the text from the classical period to today. Finally, Mair highlights previously unaddressed stylistic and statistical aspects and includes philological annotations that present new ways of approaching the intellectual and social background of the work.
The book also features a foreword by Arthur Waldron that compares and contrasts Sun Zi and Clausewitz (1780-1831).
For those who would rather read the selections below in the original format, they are also available as PDFs:
Please note that at the time of this writing, Amazon’s “search inside” function for this book is screwed up. Instead it uses someone else’s translation. So don’t order what is listed on that site as the paperback edition; because it is the wrong book. (As of February 2008 there is no paperback of Mair’s translation.) But ordering what Amazon lists as the hardback should get you the correct book (ISBN: 978-0-231-13382-1). Or order directly from the publisher should your local bookstores not have this in stock.
OK, now here are the excerpts I promised.
Key Terms
Here are highlighted only several of the more important words and subtle concepts used in the book. Other technical terms and proper nouns are defined in the notes or in the introduction. For a superb handbook of basic Chinese philosophical terms, including many that are featured in the Sun Zi, see Zhang Dainian, Key Concepts in Chinese Philosophy, trans. Edmund Ryden.
From The Art of War: Sun Zi’s Military Methods, translated by Victor H. Mair, © 2007 by Columbia University Press. Used by permission of Columbia University Press.
[Webmaster’s note: As Mair notes elsewhere, giving the pronunciations in Pinyin for Modern Standard Mandarin is “purely a convention of modern scholarship and does not reflect at all the pronunciation of Sinitic during the late Warring States period when this text was compiled.”]
bian. Variation, variety, transformation.
bing. The earliest form of the character used to write this word depicts two arms holding up an adze. The basic idea conveyed by this graph subsequently developed from the concrete and limited to the more general and abstract: weapon ? soldier ? troops ? war.
fa. Law, method, model.
bing. The earliest form of the character used to write this word depicts two arms holding up an adze. The basic idea conveyed by this graph subsequently developed from the concrete and limited to the more general and abstract: weapon → soldier → troops → war.
fa. Law, method, model.
bingfa. The combination of the previous two terms, it is usually rendered as “art of war” in English but may more literally be rendered as “soldierly methods,” “military methods,” etc. For further discussion of bingfa, see the introduction, n. 2.
gui. Deceit, deception; something contrary to the norm.
jī. Pivot, moment of change (functions somewhat like a tipping point); the instant just before a new development or shift occurs; the nodal point of a situation in flux. Jī also refers to the first, imperceptible beginning of movement in an unstable situation. In organic metaphors, it means “seed, germ.” The sage or superior man can recognize the immanence or incipience of these crucial moments before they become manifest to others. It cannot be stressed too heavily that jī by itself does not mean “opportunity” nor does it mean “crisis,” although it is closer to the latter than to the former because of the extreme instability of a given situation and the unforeseen consequences that may follow.
jì. Count, calculate; plan; intention. Another word in the Sun Zi sometimes rendered as “plan” is mou (as in the title of chap. 3), though it tends more in the direction of “scheme” or “counsel.” Depending upon the context, jì and mou may also convey the idea of “strategy” or “stratagem.”
lǐ. A traditional measure of length equivalent to 300 paces (hence “tricent” in English). It is easy to think of how long a tricent is (about a third of a mile) by recalling that the English word “mile” is derived from Latin milia, millia (“a thousand [paces]”). For those who are not familiar with miles, a tricent is equal to approximately half a kilometer.
lì. Advantage, benefit; profit, interest (the basic meaning is “sharp,” which is why the character used to write it has a “knife” radical).
mou. See jì.
qì. Unformed, energetic substrate of matter; material energy; the primal “stuff ” of the universe; configural energy. In the Sun Zi, it usually refers to the vital force, energy, or morale of the men in the army. For more information on qì and its metaphysical implications, see Mair (1990:137–38) and Zhang (2002:45–63).
qí. See zheng.
quan. Power, expedient (assessment)—exerted by the commander in the field. The literal meaning of the morpheme is “horizontal balance,” hence “weigh, judge, (exert) power / authority.” Quan is often associated with bian or qí (qq.v.).
shi. Configuration, circumstances, efficacy, inertia, power / force (of circumstances), authority, (strategic / positional) advantage. The subject of chap. 5, but also discussed elsewhere in the text, this is one of the key concepts of the Sun Zi. It is also one of the most ineffable.
tianxia. All under heaven, i.e., the empire (writ large).
wen. Civil, culture (contrasts with wu). The evolution of the primary meanings of the graph used to write this word, in simplest terms, is as follows: tattoo → pattern → culture / civilization / writing. The earliest meaning of wen as “tattoo” still survives in the expression wen shen (“tattoo the body”). By the time of the Warring States period, however, when the Sun Zi was written, tattooing had become a form of punishment, and different words were used to refer to it, wen itself having transmuted into one of the most exalted terms in the language. See chapter 9, n. 12 and the biography of Sun Bin in the introduction.
wu. Martial, military (contrasts with wen). The character used to write this word shows a shafted weapon and a foot, i.e., a man going off to fight in a war.
xing. Form, shape, disposition. One of the most important tactical concepts in the Sun Zi, it occurs with particularly high frequency in chapter 6, where it means mainly the arrangement of forces, and in chapter 10, where it signifies different types of terrain. There is another word, meaning “punishment,” that is pronounced exactly alike (xing) and is written with a very similar character that one might well expect to find in a work of strategy such as the Sun Zi, but it does not occur even once. The xing meaning “form, shape, disposition” occurs a total of thirty-one times in the Sun Zi. In stark contrast, the xing meaning “punishment” occurs a total of twenty-four times in the Wei Liao Zi, a work which has very little to say about the xing meaning “form, shape, disposition.” Thus the Sun Zi and the Wei Liao Zi, which probably coalesced at approximately the same time (the second half of the fourth century and the early third century, though with the Wei Liao Zi being slightly later) may be said to be in mutual complementarity with regard to the advocacy of these two key concepts of strategy. Clearly the Sun Zi is concerned with tactics but not punishment, and vice versa for the Wei Liao Zi. Similar analyses could be carried out for other principal concepts in all of the extant military treatises from the Warring States and Han periods.
zhan. Battle; specific military actions and engagements, in contrast to bing (q.v.), which is more general and abstract.
zheng. Used in combination with qí to signify contrasting types of warfare; variously translated as “direct / indirect,” “regular / irregular,” “conventional / unconventional,” “orthodox / unorthodox,” “ordinary / extraordinary,” and so forth. Of these two terms, the more difficult to grasp is qí, which may be thought of as signifying “odd, strange, singular, unique, craft(y)” or whatever is not zheng (“straight, upright, correct, right, orthodox, normative,” etc). In purely military applications, qí may be thought of as “special operations” or “unconventional warfare,” whereas zheng are main force deployments and maneuvers. The counterposing of qí and zheng was not restricted merely to military operations but was applied to politics and morality as well:
Rule the state with uprightness,
Deploy your troops with craft
Gain all under heaven with noninterference.
(Tao te Ching / Dao de jing, 57)
When there is no uprightness,
correct reverts to crafty,
good reverts to gruesome.
(Tao te Ching / Dao de jing, 58)
Nine1 Varieties2
This chapter addresses the question of responding deftly to contingencies and advises awareness of both the advantages and the disadvantages of any action that might be contemplated. The principle of preparedness is proposed as the surest way to avoid disaster.
Master Sun said,
The method of waging war is ordinarily that the general receives a mandate from the ruler, then assembles the army and brings together the masses. He does not encamp on unfavorable terrain; he joins with allies at terrain having a crossroads; he does not linger on forsaken terrain; he devises plans to extricate his forces from surrounded terrain; if he finds himself on desperate terrain he does battle.
There are paths that he does not take; there are armies that he does not strike; there are cities that he does not attack; there are terrains that he does not contest; there are ruler’s orders that he does not accept.3
Therefore,
the general who is versed in the advantages4 of the nine varieties of terrain5 knows how to wage war; the general who is not versed in the advantages of the nine varieties, although he may know the types of terrain, cannot gain the advantages of the terrain. If one prosecutes war without knowing the techniques of the nine varieties, although one may know the five advantages,6 one will not be able to gain the use of one’s men.
For this reason,
in his considerations, he who is wise must pay attention both to advantage and to disadvantage. By paying attention to advantage, his affairs will proceed with assurance; by paying attention to disadvantage, his troubles will be resolved.
For this reason,
that which causes the feudal lords to submit is disadvantage; that which causes the feudal lords to serve is encumbrance; that which causes the feudal lords to give allegiance is advantage.
Therefore,
the method of waging war is not to rely upon the enemy’s not coming, but to rely upon my waiting in readiness for him; it is not to rely upon the enemy’s not attacking, but to rely upon making myself invulnerable to attack.
Therefore,
there are five fatal flaws in a general: recklessness, for he may be killed by the enemy; timidity, for he may be captured by the enemy; irascibility, for he may be provoked by the enemy; incorruptibility, for he may be insulted by the enemy; solicitousness, for he may be made anxious by the enemy. In all of these respects, if a general overdoes them, it will be disastrous for waging war.
The overthrow of an enemy and the killing of a general are the inevitable consequences of these five fatal flaws. They cannot be left unexamined.7
NOTES
- There is vast controversy among Chinese commentators over the significance of “nine” in the title. Some say that it only means “a large number of,” while others contend that it literally means “nine.” In either case, there have been many proposals put forward for which particular group of nine (or many) items is intended. After careful study, the reader is invited to suggest his or her own set of nine (or many) variations. A good place to begin might be to look at chapter 11, “Nine Types of Terrain,” with which the present chapter
shares considerable overlap and resonance.
Wang Xi: “I claim that ‘nine’ is simply a very large number. The method of waging war requires infinite variations.”
Zhang Yu: “‘Variation’ is the method of not being constrained by constancy. This implies that, when one is confronting an evolving situation [i.e., something that is happening], one should follow what is appropriate and act accordingly. Whenever one is struggling with someone else for advantage, it is necessary to know the nine varieties of terrain. Therefore, this chapter comes after ‘The Struggle of Armies.'”
- The term bian may be more literally rendered as “transformations.” However, no single translation of bian is suitable for this chapter, since the term is applied to widely different phenomena, including “alternatives” and “contingencies,” aside from “varieties” and “transformations.”
- The Yinque Shan bamboo strip manuscripts (pp. 98-99) include a commentary on these five exclusionary (“that he does not”) clauses. The commentary emphasizes and explains the specific conditions under which a general may choose not to carry out certain (viz., the first four) courses of action that he would normally be expected to take. The fifth exclusionary clause subsumes the preceding four clauses: “When the ruler’s orders contravene these four contingencies, they are not to be carried out.”
- And disadvantages, of course.
- This word is missing in the Song-period Wu jing qi shu (Seven military classics) and Taiping yulan (Imperial survey of the Great Peace [reign period]) editions of the text.
- This probably refers to the advantages deriving from the exclusionary clauses iterated above and discussed in n. 3.
- Since it appears so frequently at the conclusion of a passage, the injunction “they cannot be left unexamined” would appear to be a formulaic expression in the rhetoric of the period.
Other works by Mair published by Columbia University Press include The Columbia Anthology of Traditional Chinese Literature, The Shorter Columbia Anthology of Traditional Chinese Literature, and The Columbia History of Chinese Literature.

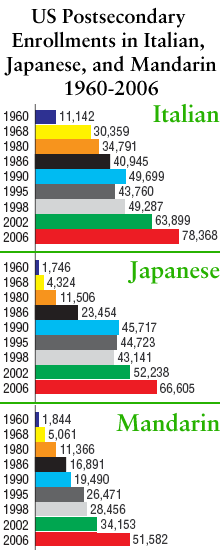 From the way the U.S. media talk about the boom in Mandarin classes, it’s easy to get the impression that Mandarin is about to become the most studied language in the United States. So I offer the following overdue reality check.
From the way the U.S. media talk about the boom in Mandarin classes, it’s easy to get the impression that Mandarin is about to become the most studied language in the United States. So I offer the following overdue reality check.